In the coming years, smart roads will likely become a critical component of transportation systems worldwide, contributing to safer, more efficient, and environmentally sustainable travel.
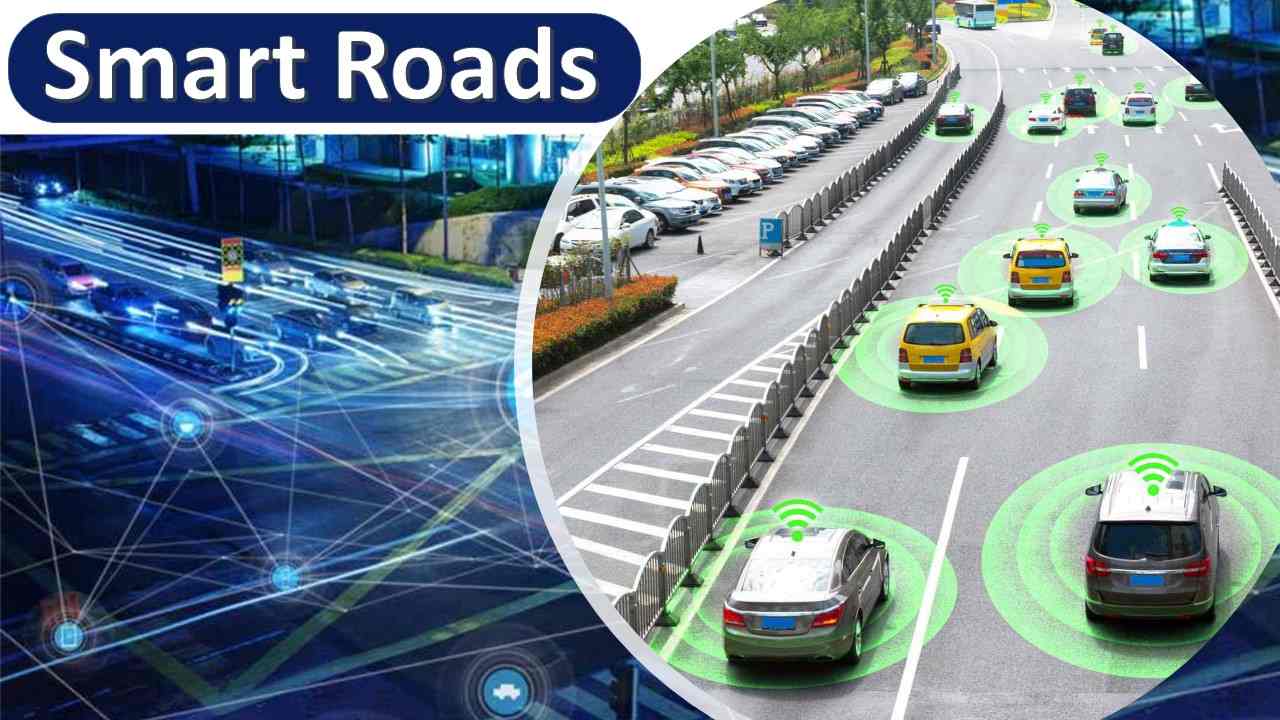 The rise of smart roads represents a significant evolution in transportation infrastructure, driven by advances in technology and the increasing need for safer, more efficient, and sustainable roadways. Smart roads integrate various technologies, such as sensors, communication systems, data analytics, and renewable energy sources, to improve the driving experience, enhance safety, and reduce the environmental impact of road networks.
The rise of smart roads represents a significant evolution in transportation infrastructure, driven by advances in technology and the increasing need for safer, more efficient, and sustainable roadways. Smart roads integrate various technologies, such as sensors, communication systems, data analytics, and renewable energy sources, to improve the driving experience, enhance safety, and reduce the environmental impact of road networks.
Here are some key aspects of the rise of smart roads:
1. Smart Traffic Management
Traffic Sensors: Embedded sensors and cameras are placed in the roadways to collect real-time data on traffic flow, vehicle speed, and congestion. This information helps optimize traffic signal timings, predict traffic conditions, and manage congestion.
Intelligent Traffic Signals: Smart traffic lights can adapt to traffic flow, changing their timing to reduce congestion and ensure smooth traffic movement. Some systems use AI to analyze patterns and adjust in real-time.
2. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
Communication Between Vehicles: V2X technology allows vehicles to communicate with each other, as well as with infrastructure like traffic signals, signs, and sensors. This communication helps drivers avoid collisions, navigate safely, and respond to road conditions more efficiently.
Autonomous Vehicles Integration: Smart roads are designed to support autonomous vehicles, providing the necessary data and communication infrastructure for self-driving cars to navigate safely.
3. Roadway Maintenance and Monitoring
Predictive Maintenance: Sensors embedded in the roadways and infrastructure can detect issues like cracks, potholes, and other road damage. This data can be sent to maintenance teams, allowing for quicker repairs and reducing the need for costly and disruptive repairs in the future.
Energy Harvesting: Some smart roads are equipped with technology that can generate energy from vehicle movements or solar panels. This energy can be used to power road lighting, sensors, or even charge electric vehicles as they travel.
4. Enhanced Safety Features
Real-Time Data Sharing: Roadways can send real-time data to vehicles, providing alerts for hazards such as accidents, weather conditions, or obstacles on the road. This can improve driver awareness and help prevent accidents.
Pedestrian and Cyclist Safety: Smart roads can include features like pedestrian detection systems, which alert drivers to the presence of people crossing the street, and dedicated lanes for cyclists equipped with sensors to ensure their safety.
5. Integration with Urban Infrastructure
Smart Cities: As part of a broader smart city initiative, smart roads can be integrated with urban infrastructure like public transportation, smart buildings, and utilities. This allows for better coordination of resources and improved urban mobility.
Data-Driven Urban Planning: The data collected from smart roads can be used to inform urban planning decisions, such as optimizing road layouts, identifying high-risk areas for accidents, and improving public transportation routes.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the rise of smart roads offers tremendous benefits, there are challenges to overcome, such as high initial costs, privacy concerns, and the need for regulatory frameworks. Additionally, as autonomous vehicles become more common, ensuring that smart road systems can support them safely and efficiently will be a key focus for future development.
In the coming years, smart roads will likely become a critical component of transportation systems worldwide, contributing to safer, more efficient, and environmentally sustainable travel.